Dog Age Calculator
How to Use the Dog to Human Years Calculator

Our Dog to Human Years Calculator is designed to help you easily convert your dog's age into human years. Here's how you can use it:
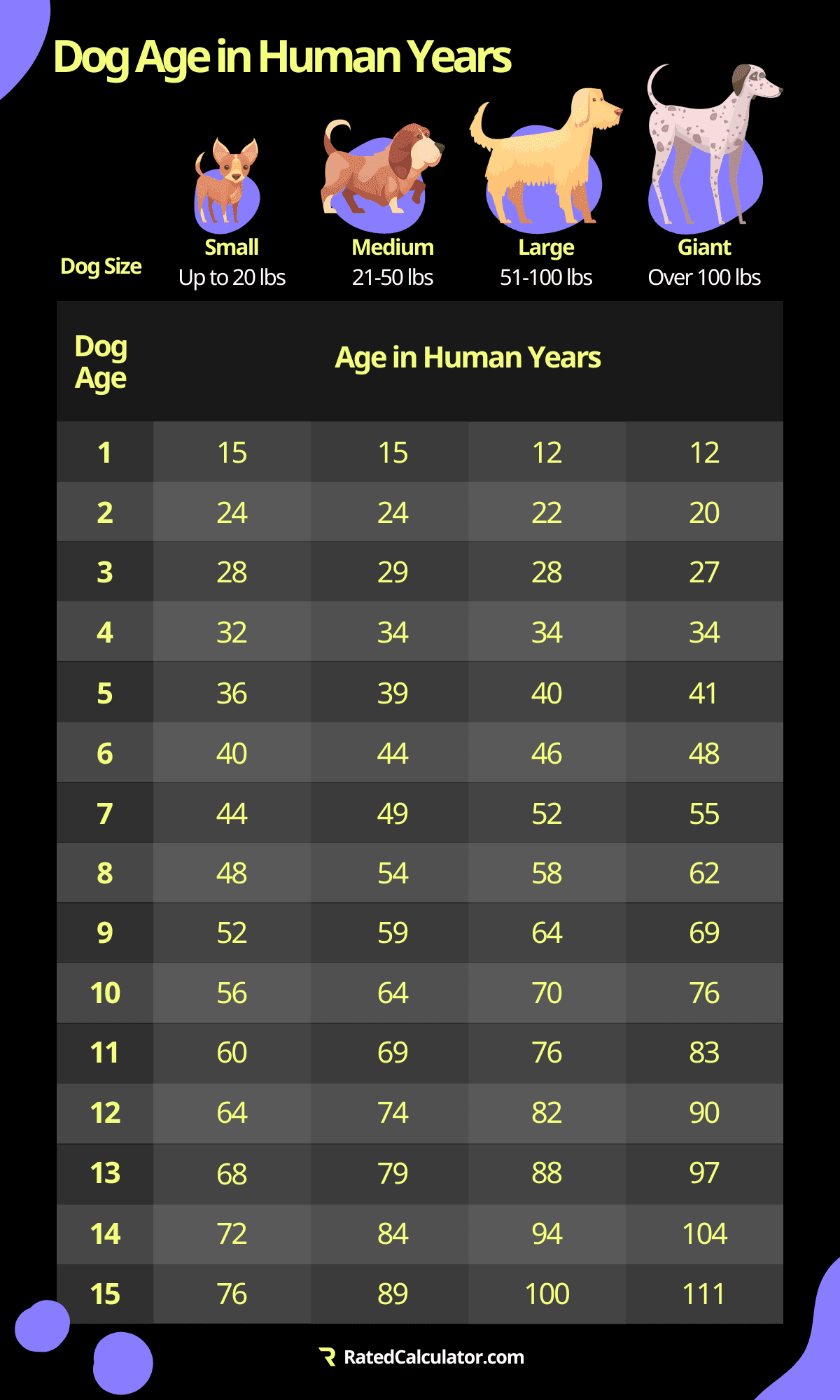
- Select Your Dog's Size: Choose the size category that best describes your dog - Small (up to 20 lbs), Medium (21-50 lbs), Large (51-100 lbs), or Giant (over 100 lbs).
- Enter Your Dog's Age: Input your dog's age in either years or months. The calculator will automatically adjust to provide an accurate conversion.
- View the Result: The calculator will display your dog's age in human years based on the selected size and age input. This helps you understand your dog's life stage compared to a human's.
Below you'll find a table showing the life stage for dogs by their age:
| Number of Actual Years | Dogs Life Stage |
|---|---|
| 0 - 1 | Puppy |
| 1 - 2 | Adolescent |
| 2 - 7 | Adult |
| 7 - 12 | Senior |
| 12+ | Geriatric |
How Do You Convert Dog Years to Human Years?
The process of converting dog years to human years has evolved over time. Here are some common methods:
- Multiplication by 7 Method: This traditional method simply multiplies the dog's age by 7 to estimate their age in human years. While easy to remember, it's not very accurate as it doesn't account for differences in aging rates among different breeds and sizes.
- Age Conversion Chart: Some charts provide a more nuanced approach by accounting for different growth stages. For example, the first two years of a dog's life are often considered equivalent to 21 human years, and each subsequent year equals 4-5 human years for small and medium dogs, and 7-9 human years for large and giant dogs.
Why Do Some Dogs Live Longer Than Others?
The lifespan of a dog can vary greatly based on several factors:
- Size and Breed: Generally, smaller dog breeds tend to live longer than larger breeds. For instance, small breeds like Chihuahuas and Dachshunds can live 15 years or more, while larger breeds like Great Danes and Saint Bernards often live around 7-10 years.
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a crucial role in determining a dog's lifespan. Some breeds are prone to specific health issues that can affect longevity.
- Health and Lifestyle: Regular veterinary care, a balanced diet, and adequate exercise contribute significantly to a dog's lifespan. Dogs that receive regular check-ups and live in a healthy environment tend to live longer.
- Environment: Dogs living in a safe, stress-free environment with good hygiene and proper care tend to have longer lifespans compared to those exposed to stressful or unhealthy conditions.
How Can You Help Your Dog Live Longer?
Here are some tips to help your dog lead a longer, healthier life:
- Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule regular vet visits to catch and treat health issues early. Routine exams can prevent and manage many conditions that could shorten your dog's life.
- Balanced Diet: Feed your dog a high-quality, balanced diet appropriate for their age, size, and health condition. Avoid overfeeding and provide appropriate portion sizes.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and keeps your dog's muscles and joints strong. Mental stimulation through training and interactive toys also keeps your dog's brain sharp.
- Dental Care: Dental health is often overlooked but is crucial for your dog's overall health. Brush your dog's teeth regularly and provide dental treats or toys to prevent gum disease and other dental issues.
- Preventative Medications: Use preventative medications for parasites like fleas, ticks, and heartworms. These parasites can cause severe health issues if left untreated.
- Safe Environment: Ensure your dog lives in a safe environment. Avoid exposing them to toxic substances, keep them away from dangerous areas, and provide a secure and comfortable living space.
References
- American Veterinary Medical Association: Pets age faster than People
- VCA Animal Hospitals: How Old is Old? Comparing Dog Age to Human Age